Master Plan
What is a Master Plan?
The Tamil Nadu Town and Country Planning Act, 1971, an Act to provide for planning the development and use of rural and urban land in the State of TamilNadu, states the Master Plan may provide for any or all of the following matters:
• the manner in which the land in the planning area shall be used;
• the allotment or reservation of land for residential, commercial, industrial and agricultural purposes and for parks, play-fields and open spaces;
• the allotment and reservation of land for public buildings, institutions and for civic amenities;
• the allotment and reservation of land for public buildings, institutions and for civic amenities;
• the traffic and transportation pattern and traffic circulation pattern;
• the major road and street improvements;
• the areas reserved for future development, expansion and for new housing;
• the provision for the improvement of areas of bad layout or obsolete development and slum areas and for relocation of population;
• the amenities, services and utilities;
• the provision for detailed development of specific areas for housing, shopping, industries and civic amenities and educational and cultural facilities;
• the control of architectural features, elevation and frontage of buildings and structures;
• the provision for regulating the zone, the location, height, number of storeys and size of buildings and other structures, the size of the yards and other open spaces and the use of buildings, structures and land;
• the stages by which the Master Plan shall be carried out; and such other matters as may be prescribed.
The URDPFI 2015 guideline describes Master Plan (Development Plan) in the following manner:
- The objective of the development plan is to provide further necessary details and intended actions in the form of strategies and physical proposals for various policies given in the time frame of these plans are generally valid over a period of 20-30 years and should be planned in phases of 5 years, for periodic reviews.
- In addition to these, the Master Plan is also meant to identify areas required to be preserved, conserved and development of areas of ecological value, natural scenery and landscape together with preservation of features, structures or places of historical, architectural and scientific interest and environmental value.
What does it lead to?
Urban areas in Tamil Nadu, as elsewhere, have grown both in size and complexity over the past decades and have become unmanageable. The need for a mechanism or a way forward to plan inclusively, to regulate and control the growth and development of urban areas has become all the more necessary. More than ever now the impact of development on the environment needs to be carefully studied. The Town and Country Planning Act, 1971, provides for preparation and implementation of Master Plans for urban areas, to ameliorate the situation in urban areas and make them a place for safe, healthy and sustainable development.
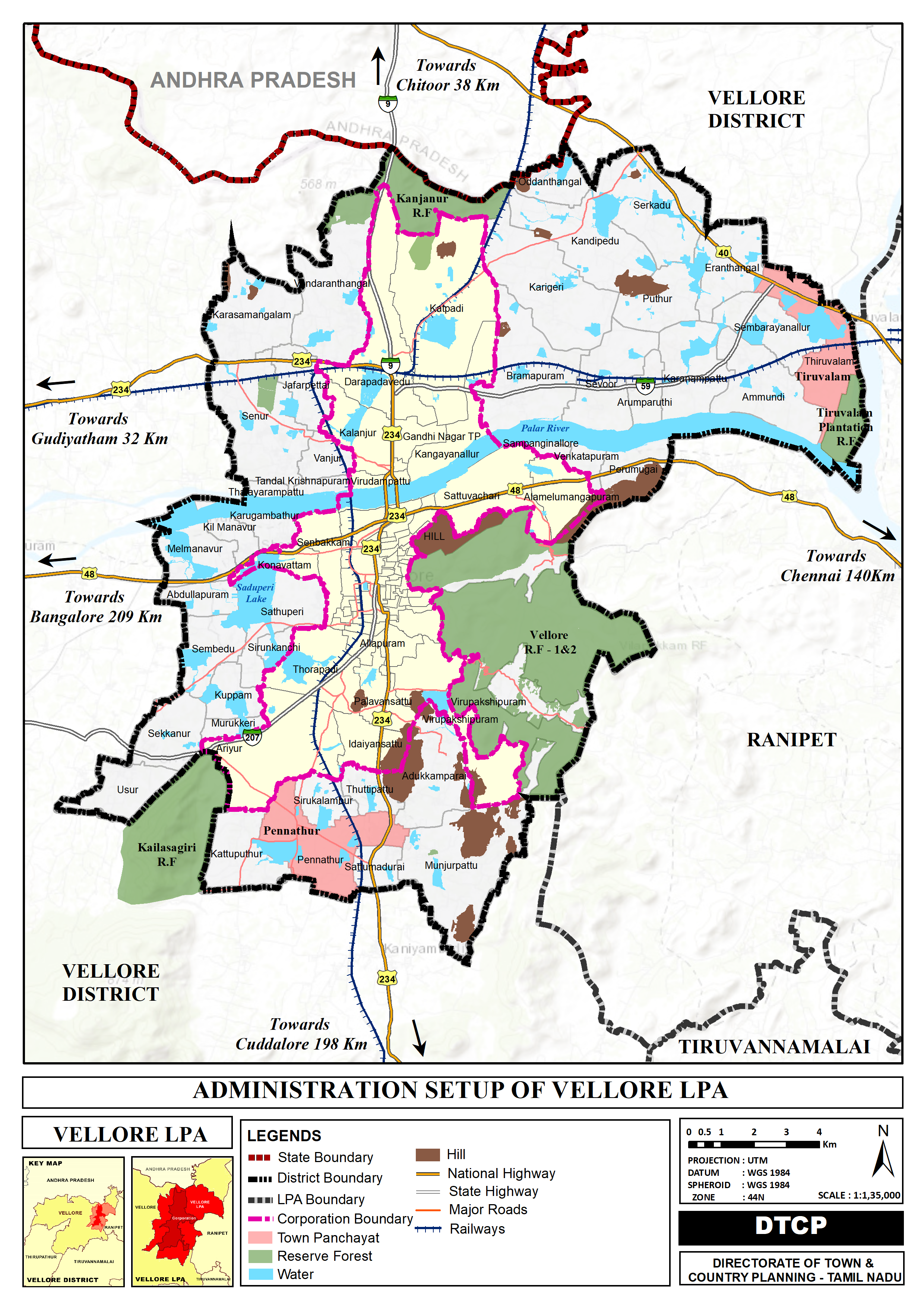
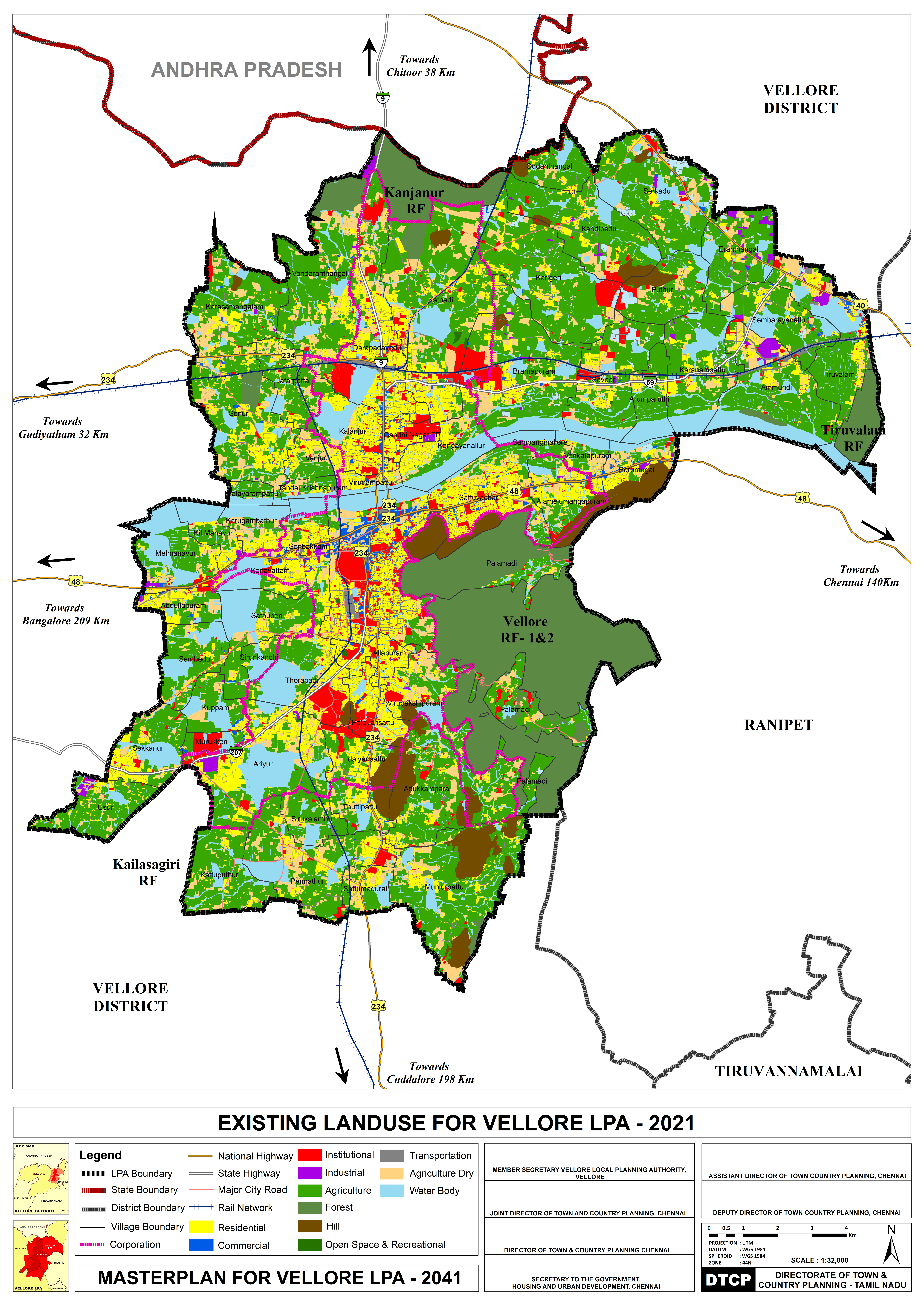
It is important to recall that Vellore is the major Institutional Hub, which comprises the educational institution and Health Care Facilities. Moreover, the Vellore LPA has 3 reserve forests and hillocks. Vellore LPA has on Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) site, Vellore fort